Natural Language Processing & Its Impact on How We Search
This article provides an introduction to natural language processing and how it works, including the tokenization and lemmatization steps. It also discusses how the Google BERT NLP uses entity mapping for semantic analysis, which has changed search, as well as how you can use NLP in SEO keyword research.
Ready to align your content with how Google actually understands language? Let’s map your brand to the entities that matter most. Contact us to make NLP work for your SEO.
What is Natural Language Processing?
According to IBM, natural language processing (or NLP) is “a subfield of computer science and AI that uses machine learning to enable computers to understand and communicate with human language.”
NLP is not a new concept. It has been discussed a lot more lately because of generative AI, which we will get to, but it also includes:
- Translating text into different languages
- Spam filters for email
- Autocomplete
- Chatbots
- Text-to-speech functionality
How Does Natural Language Processing Work?
Supervised NLP is when software is trained to respond in a certain way. In contrast, unsupervised NLP is when software uses a language model to identify the patterns in text and return a response. There are steps to this:
- NLP breaks the input sentences down to individual words (tokenization)
- NLP tags the parts of speech (nouns, verbs, adjectives, etc) from the input
- NLP simplifies words into their root form (lemmatization)
- NLP tries to disambiguate words with different meanings
- NLP identifies special entities — the name of a specific person, place or thing
- NLP searches for sentiment to determine why you are asking what you are asking
NLP in Search
Over the past dozen years, Google has released a number of algorithm updates that led to the conversational search we have today.
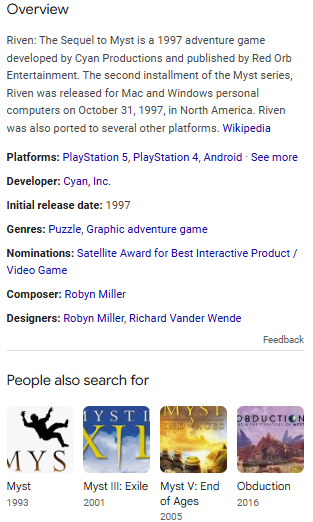
Hummingbird (2013) is when Google started trying to map entities. For example, if I search “Riven,” Google consults its index for additional information about the game.
- Year of release — 1997
- Available on — PC, PlayStation, SEGA Saturn
- Genre — Point-and-click adventure
- Reviews — 83 on Metacritic
- Developer — Cyan
- Publisher — Cyan
- Related games — Myst (prequel), Myst III: Exile (sequel), Riven (2024 remake)
Here is a high-level illustration of how Google maps the entities related to Riven.
Sometimes it shows you select information within the knowledge graph.
RankBrain (2015) marked the point where Google began applying the semantic and entity data collected through Hummingbird to actively reshape search results — using machine learning to interpret unfamiliar queries, refine relevance, and better match user intent. It helped Google interpret unfamiliar or long-tail queries and better understand intent, especially when exact keyword matches weren’t available.
BERT (2018) is the formal NLP used by Google that considers the sequence of words to derive a more accurate meaning from a query. Before BERT, you could search a series of words in any order and be served webpages that contained those words (unless they got flagged by spam filters). If you’re used to searching this way — and an entire generation of people are — there are many situations where you will need to take the time to formulate a proper question. This is an inconvenience.
Let’s talk about an example. Royce da 5’9” once rapped “do a joint or two with Joyner Lucas” on a song. The line was stuck in my head, but I couldn’t remember the song title. Before BERT, if I searched “royce joint or two with joyner lucas,” it would return lyric websites. Now, it is actively looking for meaning in the line. It returns an AI Overview stating that Royce and Joyner never collaborated on a song. It returns news articles about interactions the artists have had.
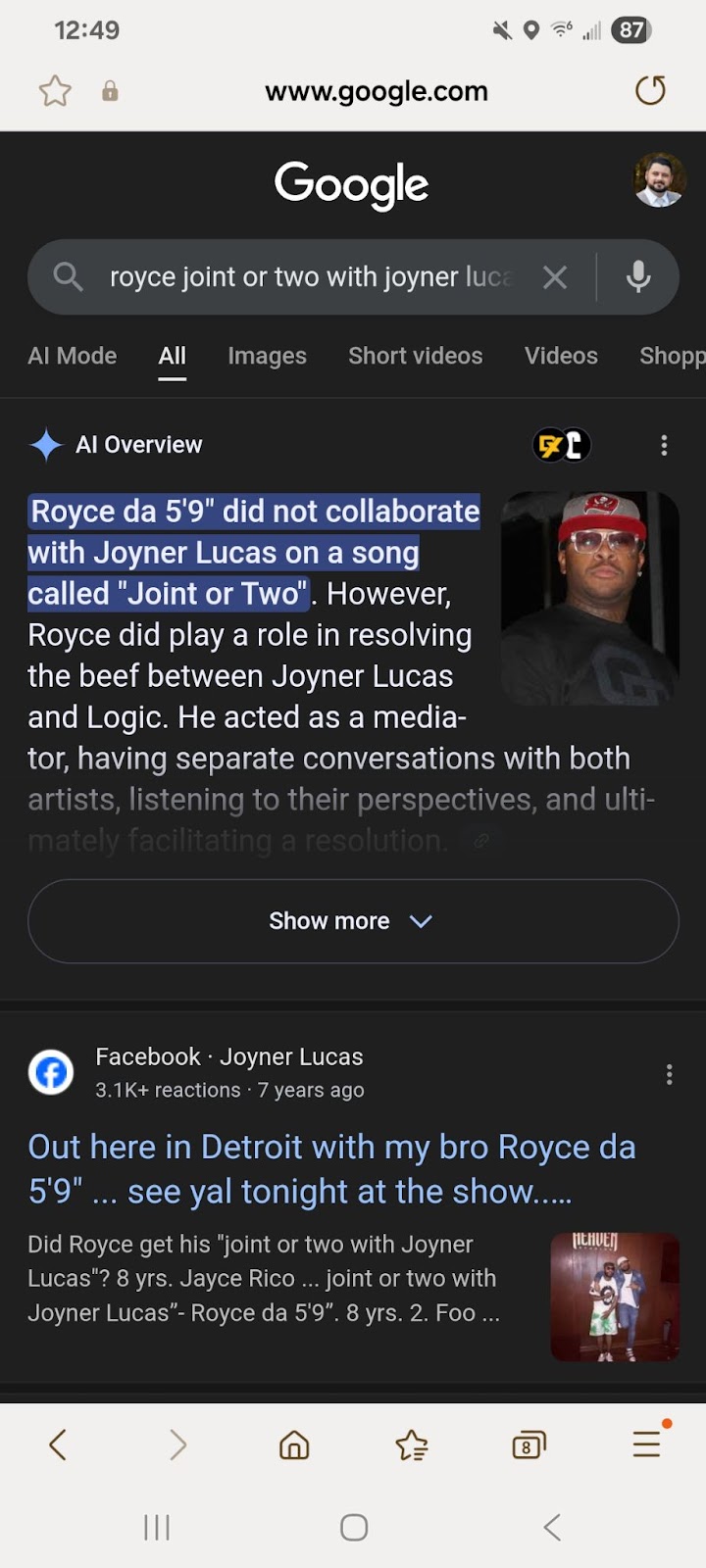
Google found meaning in my query when I just wanted it to tell me which song has the line. Now I must either:
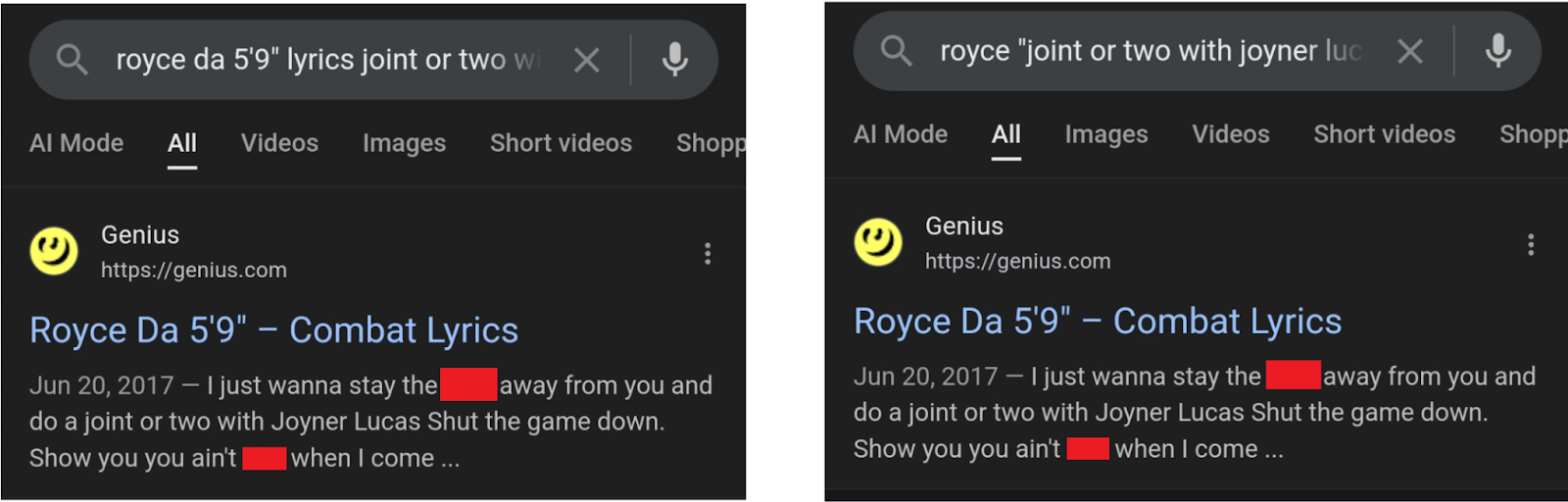
- Reform my query: [royce da 5’9” lyrics joint or two with Joyner Lucas], or
- Search with quotes: [royce “joint or two with joyner lucas”]
In both instances, Google was able to figure out my true intention, and I learned the song is called “Combat.”
Google should offer a classic search option for people who are accustomed to using its search function the traditional way, but I digress.
NLP Optimization Strategies
What’s going on? Google is trying to find deeper meaning in every query, which means that SEO strategies need to change. It is important to carefully consider how Google is perceiving every key phrase, what entities it will extract, and what the ranking websites are doing to earn their positions.
On the SERPs:
- Look at what is ranking to determine search intent (blogs, products, a mix?)
- Check for a Knowledge Graph — remember, Google classifies these data points as entities, and we want to make use of them via schema, relevant links or on-page references
On the pages that are ranking, consider:
- How are those pages organized?
- What questions are asked, and how are the answers formatted?
- Are those answers being pulled for People Also Ask?
- How aggressive is their keyword optimization?
Also, since NLP breaks down sentences into parts of speech and simplifies words to their root, simple sentences can be easier to process (at least for now).
The Future of NLP in Search
The more a piece of software knows about you, the more its NLP can be useful. Going back to the Riven example from earlier, I asked both Google and ChatGPT, “How to beat Riven?” What I meant: the 1997 point-and-click adventure game. What they thought I meant was an enemy character in League of Legends.
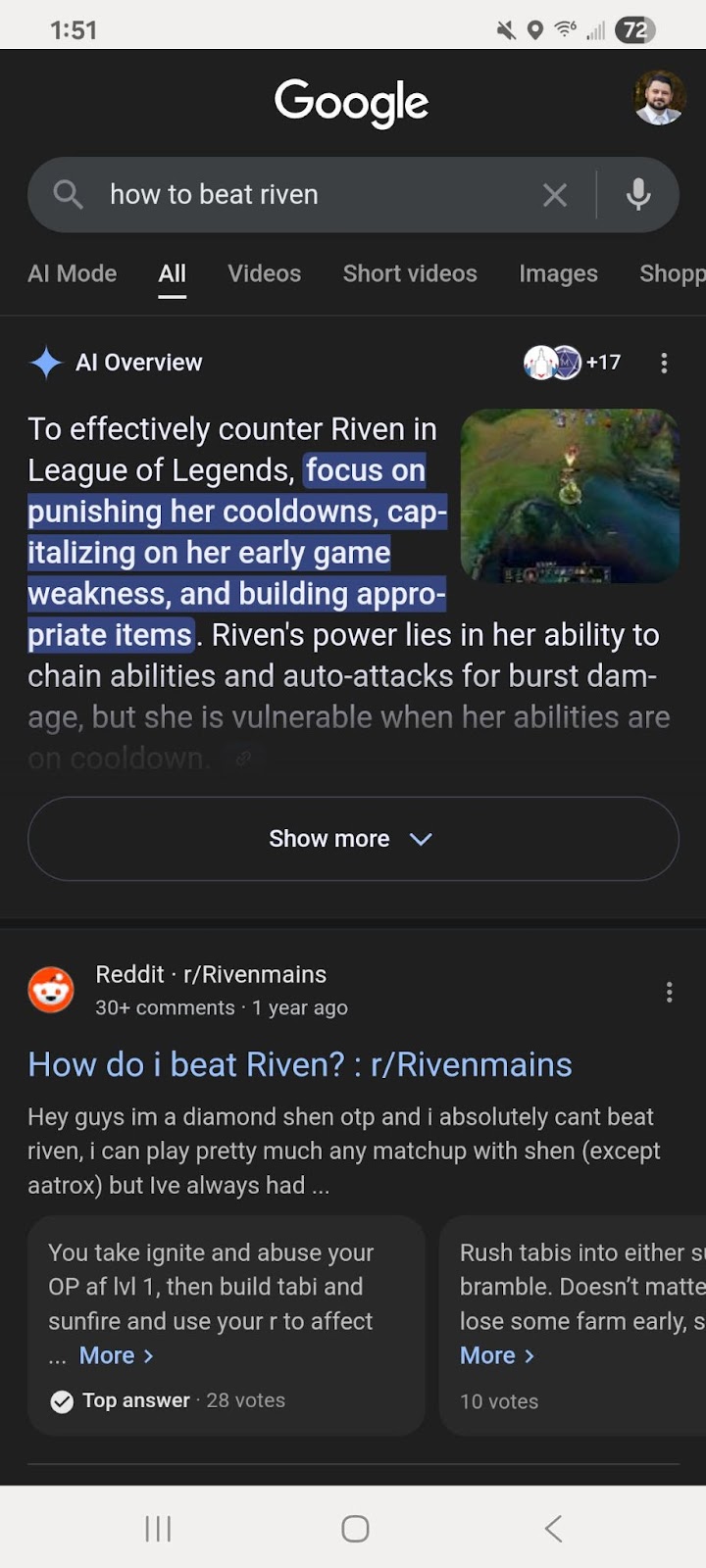
ChatGPT

The goal of NLP is to understand human language and generate human-like responses. The goal is not to give a correct response. However, if companies want us to use their software, it must be right as often as possible. So how can an NLP be right if it doesn’t understand the question? By getting to know you.
Look what happens when I tell ChatGPT “This conversation is about the 1997 game, Riven.” I asked a couple of questions first, then went back to my original question: “how to beat Riven?”
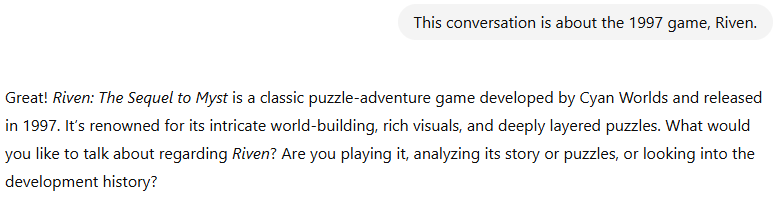
— Several Questions Later —

Same 4-word query, but now with a completely different answer.
I predict the future of NLP will be an effort to skip that first step, not by reading your mind, but by integrating everything it can find about you. YOU will be turned into an entity. To accomplish this, the push to collect your data and to sync all your devices will get worse. It is up to you whether the efficiency will be worth the invasiveness.
A Partner for NLP Optimization: If you need help figuring out where your brand fits in Google’s entity mapping or need assistance optimizing your content for NLP search, contact us to learn more about our SEO services.
The post Natural Language Processing & Its Impact on How We Search appeared first on Greenlane Search Marketing.


