Automated 404 Checking via Google App Scripts
The missing page dilemma
When a page disappears on a website, the resulting 404 error can throw a few spanners into the works, such as:
- Lost SERP listing (less organic traffic)
- Lost SEO value (damaged rankings)
- Potential dead end for users (lower conversion rate)
The trouble is that it can take days, or even weeks, to notice a 404 error, and by that time, the damage is already done.
Automating 404 checks
Before automating a solution to this issue, let’s imagine how we could check 404 errors by hand in a very boring and laborious way each day:
- Open Google Analytics 4 (GA4)
- Check the “All Pages” Engagement Report
- Change the primary dimension to “Page title and screen name”
- Filter page titles with either “404” or “Not Found” within them
- Repeat this every day, forever, just in case an issue occurs
The easiest way to automate with Google’s products is via Google App Scripts. It’s a JavaScript-based application maker which easily connects to Google product APIs, can send emails, and can run automatically on a set schedule.
You will need to have a Google Workspace account to use Google App Scripts easily.
Google App Script – 404 checker
I recommend using Google Gemini to create the script, as it’s a great platform to debug and refine scripts, as well as the obvious advantages of being much quicker and easier.
Other LLMs can struggle to get Google App Script code correct without several correction prompts, but this will improve over time with ChatGPT 5 and other upcoming AI models.
Previously, it would take 1-2 days for me to write a script like this, but with the right prompts and experience, you can boil this process down to 1-2 hours.
It’s important to use the most advanced model available (Pro 2.5+), as the quick “Flash” versions can sometimes produce invalid code or get stuck in illogical loops.
Here’s a prompt that will create the script and take you step-by-step through the process of using Google App Scripts:
“Create a Google App Script that uses the built-in connector functions ‘AnalyticsData’ to access a connected GA4 property ID using the method AnalyticsData.Properties.runReport(request, propertyName). In the script, the extra args block must be a JavaScript object literal. Download the past 30 days of daily page view metrics, filtering just page titles that contain either ‘404’ or ‘not found’, non-case-sensitive. Calculate the average number of page views over the past 30 days which meet this criterion, and create an email alert if, within the past three days, this page view count has been over double the average. In the email alert, state the GA4 account name, the property name, and the property ID for each alert. Combine all alerts into one email, and attach an in-line graph of the past 30 days’ page views using the image blob method with the ‘Charts’ service. The chart code needs to work entirely in Google Apps Script with data arrays, without needing any Sheet ranges. Add a red line to the graph which shows the threshold amount for when the alert will be activated. For the script variables of property ID, email address, lookback window (default: 3 days), and alert threshold (default: 2 times), add them to the top of the code with instructions on how to use them. Imagine that this is my first time using Google App Scripts, so provide clear instructions on how to perform each step and ask questions at the end of each future prompt to elicit a progress response and further questions.”
Follow the instructions to the letter, and you will get onto Google App Scripts and will need to enable these two APIs in the Services section:
- Google Analytics Admin API
- Google Analytics Data API
Don’t forget to set a daily trigger also, so you never miss out on any 404 issues:
If you ever get stuck or encounter an error message, then copy and paste it into the same Gemini chat, and it’ll help you get around any issues.
404 checking script variables to set
There should be four variables to set within the code:
-
- Email address – The email address (or addresses) to send the alert to
- Lookback window – How many days to look back upon for 404 anomalies. As GA4 can take over a day to process all data, I recommend keeping this to 2 or 3 days
- Alert threshold – The spike threshold, e.g. 3 = 3x average. Set this to a low number, such as 1.5 for many alerts, or a high number, such as 3 for major alerts only
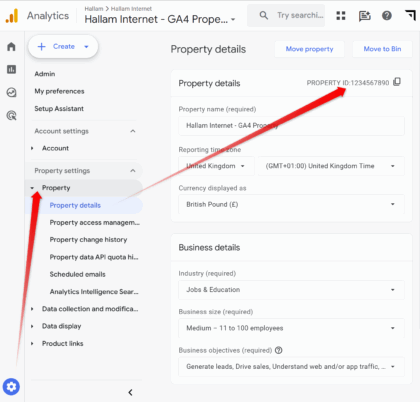
- GA4 property ID – This can be found on GA4 via Admin > Property > Property Details (see below):
Testing the alert email
You might have to wait a long time for an actual 404 alert email, so you can lower the alert threshold to, say, 0.1 to trigger it every time the script is run.
You should then receive an email alert which shows the affected property along with stats and a chart showing the 404 page views and threshold level:
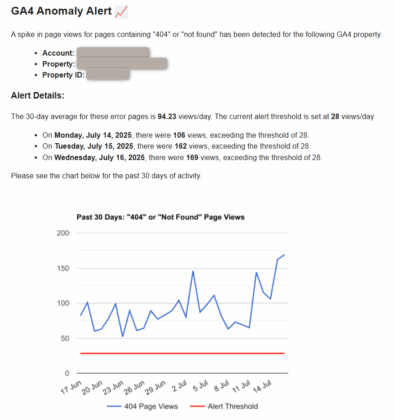
Once this is confirmed, you can reset the threshold to somewhere between 1.5 and 3.0 to only alert once there is an actual issue.
Conclusion
With this script running, you’ll be alerted whenever a 404 error arises on your GA4 property within 1 or 2 days after the event, just in time to avoid the page being de-indexed.
If you need a quicker 404 response, then we recommend using GA4 live streaming export with Big Query, which gathers data in just a few minutes in an SQL format:

The post Automated 404 Checking via Google App Scripts appeared first on Hallam.


