How to Build a Powerful Marketing Funnel (Step by Step)
Updated September 2023.
The key to automating a consistent flow of qualified leads is setting up a quality marketing funnel.
By guiding potential customers through a series of stages, from awareness to conversion, well-crafted marketing funnels can increase conversions, drive revenue and create loyal customers.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll show you how to do that. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to optimize your existing funnel(s), this guide will help you create a simple marketing funnel that best fulfills your needs.
Detailed Five-Stage Funnel
The five-stage marketing and sales funnel model is widely used in preparing a marketing strategy because it maps out the entire customer journey.
The different stages help businesses create targeted strategies and content for each phase, from initial awareness to building and maintaining customer loyalty. Let’s now understand each marketing funnel stage in detail.
Stage 1: AWARENESS – Problem/Need Recognition (ToFu)
Recognizing that you have a problem is the beginning of the buying process. This is the awareness stage.
If you don’t know you have a problem, why would you purchase a solution for it? For example, you may have gum disease, but if you don’t see or feel anything out of the ordinary in your mouth, it won’t even occur to you to do an online search for gum disease.
Or, if your furnace goes out in the middle of winter, you immediately know that you have an issue and will quickly jump to the next step (information search) in the buying process. You may do a little bit of research, but because your problem is so pressing, you won’t take long.
Other products or services will require much more education. An example might be purchasing a pharmaceutical drug. In this case, a person may recognize a physical symptom (“problem”), but it might persist for some time before they take action and look for a solution.

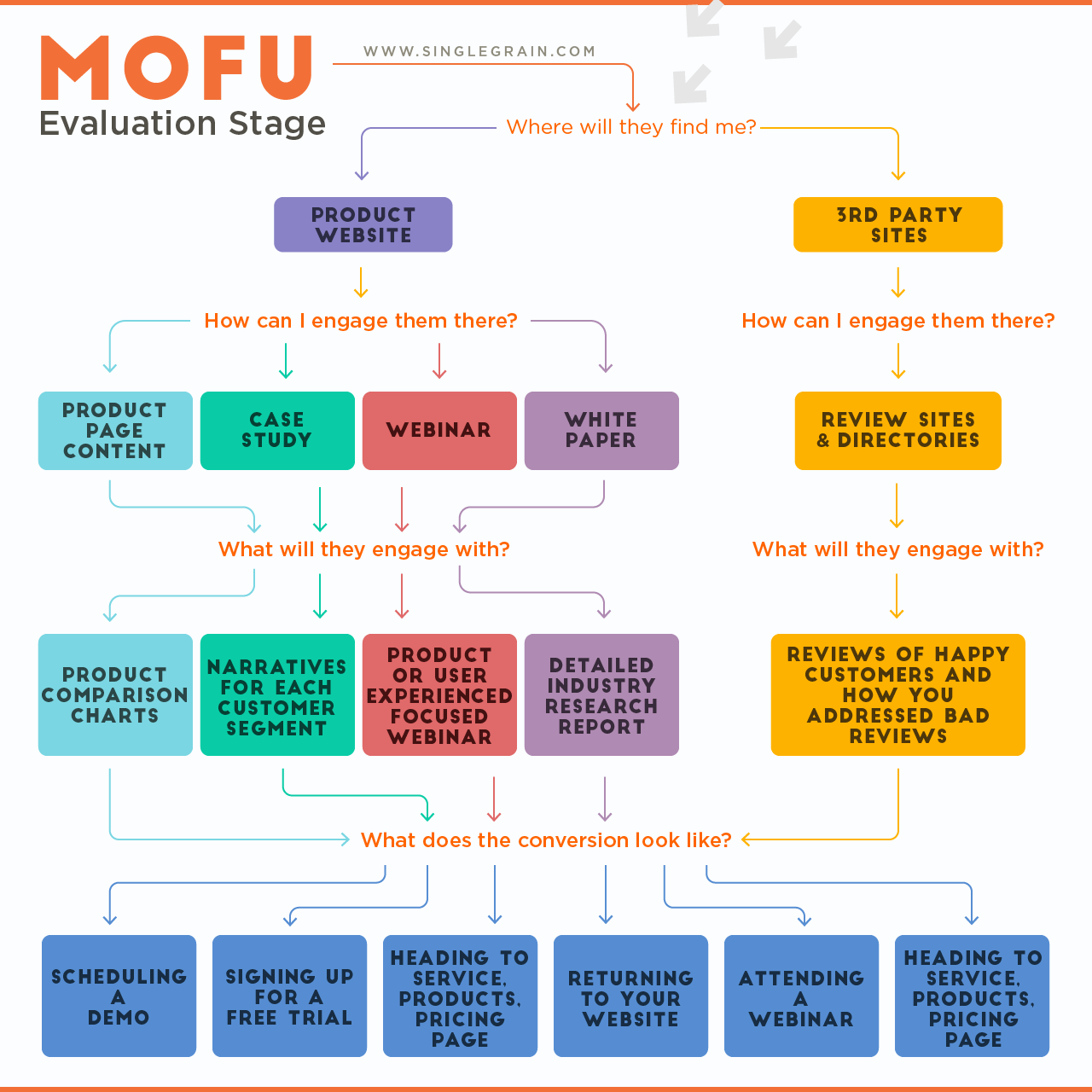
Stage 2: INTEREST – Information Search (MoFu)
Recognizing a problem or need is the step that triggers a search for more information and brings potential leads to the second stage of the funnel. The strategies used to gather information tend to vary based on the size and scope of the purchase, for example:
- Recognizing that you’re hungry might result in a quick Yelp search for restaurants in your area.
- Deciding which provider to hire to install a new in-ground pool at your home will involve doing some search engine querying, calling around, reading customer reviews, visiting showrooms and talking with salespeople.
At this point, people aren’t looking for promotional content; they’re looking to learn more about potential solutions for their needs.
Stage 3: CONSIDERATION – Evaluation of Alternatives (MoFu)
Once customers are aware of a solution, the next step is to compare the alternatives that your article or ad has discussed.
Again, the time spent in this stage will vary based on the type of purchase being contemplated. Choosing a restaurant might be as simple as deciding, “Well, I feel like Chinese food, not Mexican, tonight.”
But say the customer is evaluating marketing automation programs to help improve the marketing and sales funnel they created. Because these programs can require investments of $1,500 a month, they’re likely to undergo a much more careful and thorough evaluation process. They might:
- Seek out referrals
- Request free trials of the different systems they’re considering
- View training videos to get a feel for how each system will perform
- Request online demonstrations with each company’s representatives
If you’re running a marketing services business, you might create content about:
- How to choose a marketing agency
- Agency pricing guides
- Whether a company should go with a contractor or hire in-house
(The above examples are non-promotional, educational content resources we’ve created for our readers who are considering hiring digital marketing agencies.)
Note that prospects reaching this stage are more serious about making a purchase than customers doing initial research. So, if you have limited resources, you don’t have to start at the top of the funnel.
Instead, start by targeting only the bottom-of-the-funnel prospects for maximum conversions from minimum effort.
Stage 4: CONVERSION – Purchase Decision (BoFu)
The purchase decision is the natural conclusion of the preceding three stages. The potential customer has determined that they have a problem, investigated their options, decided which one is best for them … and now they’re getting ready to pull out their wallets.
At this conversion stage, optimizing your website for conversions (CRO) is an excellent way to increase sales. You can also provide risk-free trials, money-back guarantees and similar offers that make purchasing your product or service a no-brainer.

Stage 5: LOYALTY – Post-Purchase Behavior
One more thing: The customer journey isn’t over just because a purchase has been made. What happens after the sale is also important.
If your new customers are greeted by a thoughtful onboarding process, personal attention and all the resources they need to use your product successfully, they’re more likely to become loyal customers. They’ll happily give recommendations and product endorsements.
On the other hand, if your new customers experience disappointment after their purchase, they’re more likely to request refunds, write negative reviews and recommend that others in their social circles purchase from your competitors.
If you have a great product that solves a problem, and you make the whole customer journey easy and pleasurable, post-purchase behavior will take care of itself.
There are certain actions you can take to help facilitate better post-purchase behavior, i.e., retention:
- Creating FAQ content
- Adding testimonials from brand advocates
- Making it easy/easier to get customer support
- Soliciting feedback on the buying process
Related Content: 5 Ways to Re-Engage Those Long-Lost Customers
AIDA: The Four-Stage Content Creation Funnel
There’s another way to remember the stages of the marketing funnel and match them to content creation: with the acronym AIDA.
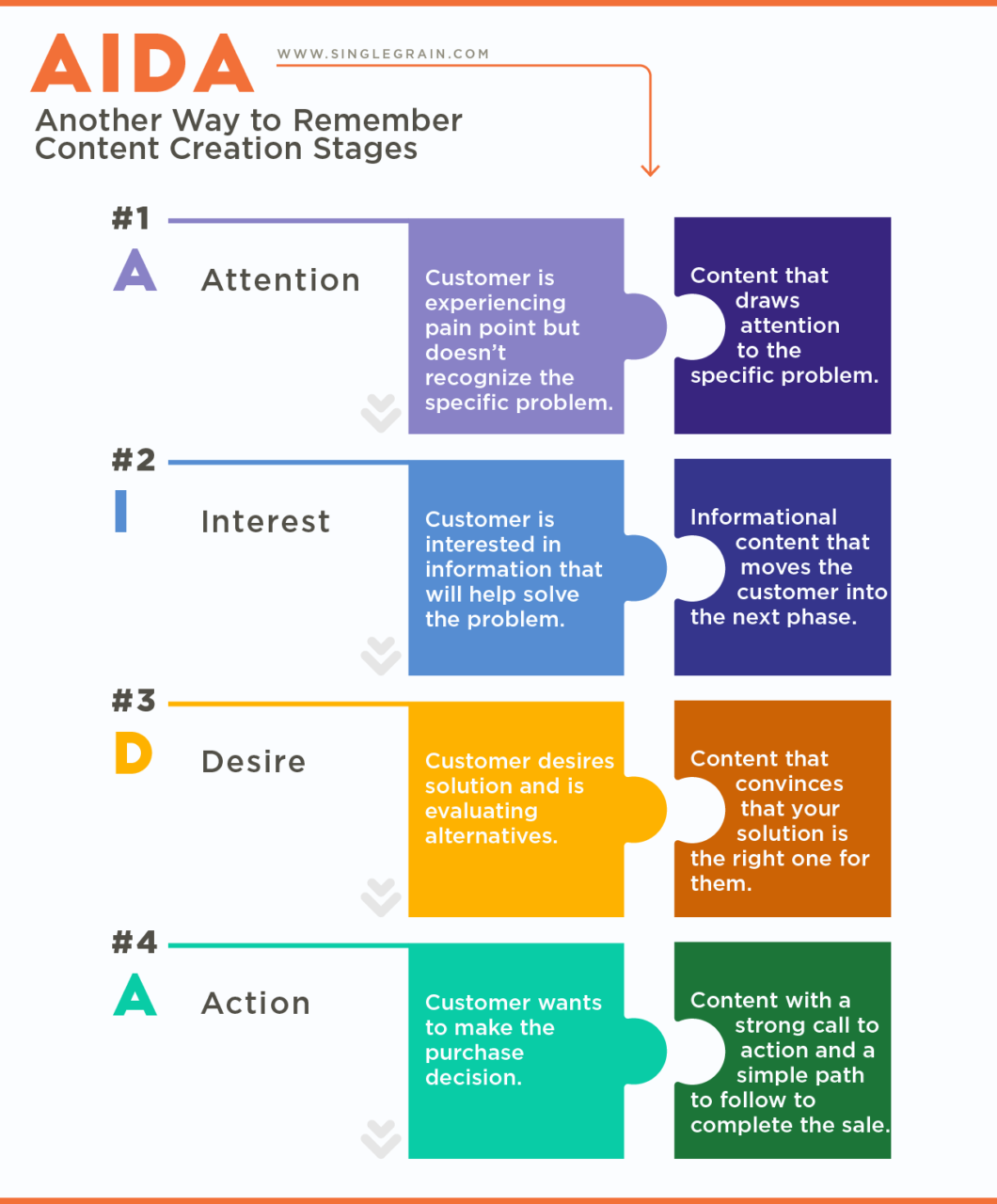
AIDA is a classic marketing framework that represents a four-stage content creation funnel. It stands for Attention, Interest, Desire and Action. This model has been widely used in marketing and advertising for over a century.
Let’s take a look at the different stages of the AIDA framework to attract prospective customers:
Attention
- Goal: Grab the audience’s notice.
- Approach: Use compelling visuals or striking headlines.
- Example: Include an engaging image or a captivating headline in an ad.
Interest
- Goal: Foster curiosity and intrigue.
- Approach: Offer valuable and relevant information.
- Example: Explain the benefits of your product or service in a way that piques curiosity.
Desire
- Goal: Stoke a strong desire or need.
- Approach: Emphasize emotional and practical benefits.
- Example: Showcase how your offering fulfills desires or provides unique advantages.
Action
- Goal: Encourage the audience to take a specific action.
- Approach: Include a clear and compelling call to action.
- Example: Use a “Buy Now” button or a “Sign Up” link to prompt immediate engagement.
The AIDA content creation funnel provides a structured approach to content marketing tactics, guiding marketing and sales teams in effectively moving target customers through the stages from awareness to action.
Whether you prefer the traditional marketing funnel stages or the acronym AIDA, the results are the same:
- Customers enter the marketing funnel.
- They choose to either purchase from you or move to an alternative solution.
- The purchase concludes the stages of the conversion funnel.
Although most people enter the funnel at the top, not everyone does; some will enter at subsequent stages. Regardless, the process remains the same.
How to Build a Marketing Funnel for Your Content
Now that you know how people make decisions, it’s time to create your marketing funnel. We’ll use the slightly simpler AIDA stages for our builder example.
As mentioned earlier, one of the main points is choosing which marketing channels to include in your marketing efforts. To start with, you can use this template for marketing funnels. Ideally, you’ll want to use all of the marketing channels below:

Unfortunately, the reality is that few companies have the resources to tackle all of these channels (podcasting, paid search, social media, email marketing, newsletters, e-books, white papers, etc.) effectively.
So, although we’ll discuss each stage of the marketing funnel, keep in mind that it might be more effective to start at the bottom of the funnel and work your way up, since customers already at the bottom of the funnel are much more likely to make a purchase and become repeat customers.
Overview of the Steps to Create a Marketing Funnel
By understanding and implementing the steps involved in creating successful marketing funnels, you’ll be able to methodically guide potential buyers through a well-defined customer journey, and increase the likelihood of funnel conversion and long-term customer relationships.
Here’s an overview of the steps required to build a successful marketing funnel:
- Identify Your Audience: First, to create an effective marketing funnel, thoroughly understand your target audience’s demographics, behaviors and preferences so that you can tailor your marketing efforts accordingly.
- Set Objectives: Clearly define specific and measurable marketing objectives that align with your business goals, ensuring that they are achievable, relevant and time-bound to guide your funnel strategy effectively.
- Choose Channels: Select the most appropriate marketing channels and platforms based on your audience’s preferred communication methods and your objectives, allowing you to reach potential customers where they are most active.
- Create Content: Craft compelling and relevant content for each stage of the funnel, ensuring that it addresses the needs and interests of your target audience, guiding them through their decision-making journey.
- Lead Capture: Develop strategies to capture leads’ contact information — such as email addresses or phone numbers — using techniques like sign-up forms, landing pages or gated content to initiate further engagement.
- Nurture Leads: Build relationships with leads by providing valuable information and addressing their questions or concerns, gradually guiding them toward a decision to engage with your product or service.
- Conversion Strategies: Implement tactics and incentives that encourage prospects to take specific actions — such as making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter or requesting a demo — to move them from prospects to customers.
- Measure and Optimize: Continuously monitor the performance of your marketing funnel, analyzing metrics and data to identify areas for improvement and fine-tune your strategies for better results.
- Post-Purchase Engagement: Maintain ongoing engagement with customers after purchase by providing exceptional post-sales support, offering loyalty programs, and soliciting feedback to foster long-term relationships and encourage repeat customers.
Now that you’ve got a good idea of what a digital marketing funnel entails, let’s dive into the funnel stages (using the simpler AIDA funnel).
Stage 1: Problem/Need Recognition (ToFu)
Your customer may be vaguely aware that they have an issue, though they may not be actively looking for a solution.
For example, let’s say you sell vests that keep outdoor workers cool in the summertime. Your target audience may find that being hot is annoying, but they may not be aware that anything exists to solve it, so they likely won’t even be thinking of looking for a solution.
But, if they see or hear an advertisement for a cooling vest, they might have an “aha!” moment and do some further research on the subject. So, capturing people at this stage generally consists of outbound marketing or advertising.
Keyword Strategy for ToFu
At the problem/need recognition stage, focus on keywords related to general pain points, symptoms or issues that your product or service can address. Use terms that capture the audience’s problem awareness but not necessarily the product-specific solution.
Some examples of keywords at this stage related to different niches can be:
- Signs of hair loss in men
- How to reduce back pain
- Managing stress at work
- Symptoms of dry skin
- Ways to improve home security
- Understanding financial stress
- Impact of poor posture on health
- Preventing kitchen fires
Best Channels for ToFu
- Podcast Advertising: Reach audiences who are interested in your industry or field, and create ads that spark recognition of the problem.
- Influencer Marketing: Partner with influencers who can discuss common issues that your product or service addresses in their content.
- Paid Ads (Facebook, YouTube, Google, etc.): Craft ad campaigns that focus on problem awareness rather than direct product promotion.
- Radio Ads: Use radio advertising to introduce the pain points your solution can resolve, targeting relevant demographics.
- TV Ads: Create TV commercials that highlight the challenges your audience faces without explicitly selling your product.
Examples of Content for ToFu:
- Blog posts addressing common challenges or issues in your industry
- Informative videos or infographics highlighting common pain points
- Educational podcasts discussing industry challenges without directly promoting your solution
Purchase Intent: This stage is the furthest from purchase intent, so prioritize optimizing your website for Stage 4 (conversion) and gradually work backward through the marketing funnel stages.
Action Tip: Investigate where and how your competitors have been advertising the longest, as it may indicate effective channels for raising problem awareness.
Stage 2: Information Search (MoFu)
Now that your customers are interested in finding a solution to their problem, the next step is to create the information they want to know.
Keyword Strategy for This Stage
In the information search stage, target keywords related to educational and informative content. Focus on answering questions and providing insights related to the audience’s problem or need.
Here are some keyword examples for the middle-of-the-funnel stage:
- How to [solve a problem or address a need]
- Tips for [common issue or pain point]
- Guide to [relevant topic]
- Best practices for [related subject]
- Solutions for [specific problem]
- Benefits of [related solution or approach]
Best Channels for This Stage
- Content Marketing: Offer in-depth information and insights about how your products or services solve different pain points of your target audiences.
- SEO: Optimize your content to rank for informational keywords that your audience is likely to search for.
- Social Media: Use your social platforms to share educational content that addresses your audience’s early-stage pain points.
Examples of Content at This Stage:
- Create blog posts addressing fundamental topics related to your industry or product.
- Establish a YouTube channel focusing on “how-to” guides, “what is” explanations and other educational content.
- Develop search-engine-optimized content that ranks well for specific informational queries.
- Share social media posts that inform users about basic pain points relevant to your product or service.
Purchase Intent: This stage is still relatively distant from purchase intent. Prioritize optimizing your website for Stages 4 (conversion) and 3 (desire) before focusing on Stage 2.
Action Tip: Discover what people typically search for when they first recognize a problem or need, and create content that answers those initial questions effectively.
Stage 3: Evaluation of Alternatives (MoFu)
At this stage of the marketing funnel, your customers know that a solution to their pain point exists. So, the next stage (if they continue down the funnel; most will simply bounce at this point until the pain grows strong enough that they take action) is to evaluate different solutions.
Keyword Strategy for This Stage
In this stage, target keywords that indicate strong purchase intent. Focus on keywords related to your product or service, competitor alternatives and pricing comparisons. Here are some example keywords for this stage:
- [Product/service] reviews
- [Product/service] vs. [competitor]
- Best [product/service] for [specific use case]
- Top-rated [product/service]
- [Product/service] pricing and plans
- Is [your product/service] worth it?
- Discounts on [product/service]
- [Product/service] deals and offers
- [Your brand] [product/service] coupon code
Best Channels for This Stage
- SEO & Content Marketing: Publish content that highlights the advantages of your solution over competitors and addresses purchase-related queries.
- Review Campaigns: Encourage customers to leave reviews on platforms such as Google My Business, Yelp or industry-specific review sites.
- Retargeting Ads: Reach out to users who have shown interest by visiting your website or specific product pages.
Examples of Content at This Stage:
- If you are marketing for a product like FreshBooks, create content optimized for keywords like “best accounting software for small business.”
- Create landing pages that have a high-quality score when you bid on competitor keywords like “QuickBooks” to capture users actively comparing accounting software options.
- Optimize your pricing page through link-building efforts and internal linking. Run retargeting ads that target users who have visited your pricing page.
- Add social proof to your site. Send out customer surveys, and request reviews from happy and loyal customers to build social proof.
Purchase Intent: Purchase intent is very high at this stage, making it a top priority for optimization. If resources are limited, focus on fully optimizing this stage before moving up the marketing funnel.
Action Tip: Take full advantage of the conversion stage’s high-quality audience by exhaustively optimizing every step in this stage before addressing earlier marketing funnel stages.
Stage 4: Purchase Decision (BoFu)
This is the most important stage: when you will convert the prospects into buyers. By this stage, potential prospects are already aware of your brand, and they have done all their research. Now, their intent is to buy, and your strategy should be to make the process as smooth as possible.
Keyword Strategy for This Stage
In this stage, your keyword research strategy should revolve around commercial keywords that express clear purchase intent. Focus on specific product or service keywords, as well as transactional keywords like “buy” or “purchase.”
Here are some example keywords for this stage:
- Buy [product/service]
- [Product/service] for sale
- [Product/service] pricing
- Discounted [product/service] price
- [Product/service] coupon code
- Free trial of [product/service]
Best Channels for This Stage
- PPC Marketing: Leverage pay-per-click (PPC) advertising on platforms like Google Ads and social media to target as many leads as possible who are actively searching for specific products or services you sell.
- Email Marketing: Send reminders, FAQs and support information to facilitate the purchase process.
- Remarketing Ads: Run display ad campaigns to leads who have previously engaged with your website or products. This will remind them of your offerings and encourage them to complete their purchase.
- Webinars and Demos: Host live or on-demand webinars and product demonstrations to showcase the value of your products or services and address any remaining concerns.
Examples of Content at This Stage:
- Develop comprehensive product or service pages that provide detailed information, pricing and options for potential buyers.
- Create articles or infographics comparing the pricing, features and benefits of your product/service against competitors or alternatives.
- Showcase real customer testimonials, reviews and success stories that highlight the positive experiences others have had with your business.
- Promote special offers, discounts or bundles for a limited time to encourage immediate purchase decisions.
- Provide step-by-step guides on how to make a purchase, including instructions for navigating your website, applying discounts and completing the order process.
Purchase Intent: People are ready to make a purchase and just want reassurance of the value you will provide them. This should be a priority after Stage 3 (usually, if you nail Stage 3, they won’t have many objections).
Action Tip: You can simply hire a CRO expert, or you may want to try different versions of your sales/pricing page to see which one converts the best.
Dive Deeper:
* What’s the Right Content for Each Stage of the Marketing Funnel?
* 17 Effective SEO Techniques to Drive Organic Traffic in 2023
* Why You Should Use Long-Tail Keywords in Your SEO Campaign
Which Marketing Funnel Metrics Should I Track?
So now you’ve created your funnel and defined exactly how your prospects will interact with it. The final step in the process is to figure out which metrics you’ll track to determine how well your funnel is functioning.
Top-of-the-Funnel Metrics (Awareness)
- Traffic Volume: This measures the total number of visitors to your website or landing page. In the top-of-the-funnel stage, a high traffic volume is crucial because it indicates that your content or marketing efforts are successfully reaching a broad audience.
- Source of Traffic: This metric identifies the channels from where visitors are coming to your website: search engines, social media, referral sites, direct visits, etc. Understanding this helps you assess the effectiveness of your marketing channels. It enables you to allocate resources to the platforms that generate the most awareness and adjust your marketing strategy if certain sources are underperforming.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): This is the percentage of users who click on your website in the search results compared to the number of total users who view it. It measures the effectiveness of your content in capturing the interest of your audience. A higher CTR indicates that your messaging resonates with users and encourages them to explore further, a critical aspect of moving prospects through the marketing funnel.
- Impressions: Impressions refer to the total number of times your content or ad is displayed to users. In the awareness stage, impressions matter because they signify the reach of your marketing efforts. A high number of impressions suggests that your brand and content are gaining exposure, even if users haven’t engaged with them yet. It’s a key metric for evaluating brand visibility.
- Engagement Rate: Engagement rate measures the level of interaction or participation users have with your content: likes, shares, comments and other social media interactions. While awareness is the primary goal in the ToFu stage, engagement rate helps you gauge the quality of that awareness. Higher engagement suggests that your content is resonating with users, potentially leading to deeper interest and consideration as they progress through the marketing funnel. It also indicates the effectiveness of your content in connecting with your audience.
Middle-of-the-Funnel Metrics (Consideration)
- Time on Page: This measures the average amount of time that users spend on a specific web page or piece of content. In the MoFu stage, time on page is important because it indicates the level of engagement and interest users have in your content. A longer time on page suggests that users are considering the information you’ve provided, which can be a sign of their growing interest and readiness to explore your offerings further.
- Bounce Rate: This calculates the percentage of users who navigate away from your site after viewing only one page. For MoFu, a lower bounce rate is ideal. A high bounce rate can indicate that visitors are not finding the content engaging or relevant to their needs. By reducing bounce rates, you increase the chances that users will continue to explore your site and move closer to conversion.
- Page Views Per Visit: This metric measures the average number of pages a user views during a single session. A higher count per visit suggests that users are actively considering multiple pieces of content on your site. This indicates deeper engagement and a greater interest in your offerings, which aligns with the MoFu goal of nurturing prospects who are exploring their options.
- Lead Conversion Rate: This measures the percentage of visitors who take a specific action to become sales-qualified leads, such as signing up for a newsletter or downloading a gated resource. It’s a direct indicator of how well your content and offers resonate with users in the consideration stage. A higher conversion rate indicates that your content effectively guides prospects toward providing their information, demonstrating their interest in your solutions.
- Cost Per Lead (CPL): This metric calculates the amount of money spent on marketing campaigns to generate one new lead. CPL is crucial in the MoFu stage because it helps assess the efficiency of your lead generation efforts. Lower CPL indicates cost-effective strategies for attracting and nurturing leads. By optimizing this metric, you can allocate resources efficiently to continue nurturing potential customers as they move toward the decision stage of the funnel.
Bottom-of-the-Funnel Metrics (Conversion)
- Conversion Rate: This is one of the important metrics that measures the percentage of prospects who take a desired action, such as making a purchase, completing a sign-up or requesting a demo. In the BoFu stage, conversion rate is crucial as it directly reflects how effectively you’re turning leads into paying customers. A higher conversion rate indicates that your strategies for persuading and closing deals are successful.
- Cost Per Acquisition (CPA): CPA calculates the average cost of acquiring a new customer through your marketing efforts. CPA is vital because it helps evaluate the efficiency of your marketing spend in acquiring new customers. A lower CPA indicates cost-effective strategies for converting leads into paying customers, making your marketing budget more efficient.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): This measures the total revenue that a customer is expected to generate over their entire relationship with your business. CLTV is crucial in the BoFu stage because it provides insight into the long-term value of each customer. Maximizing CLTV through successful conversions ensures sustainable growth and profitability for your business.
- Sales Cycle Length: This metric measures the average time it takes to convert a lead into a paying customer, from initial contact to final sale. Understanding the sales cycle length is valuable for assessing the efficiency of your conversion process. Shortening the sales cycle can lead to faster revenue generation and improved resource allocation.
- Revenue Per Customer: This calculates the average amount of revenue generated by each customer during their relationship with your business. Revenue per customer is essential in evaluating the value of individual customers. It helps identify opportunities for upselling, cross-selling and maximizing the financial return from each conversion, which is critical in the BoFu stage for maximizing profitability.
Post-Purchase Stage Metrics (Retention)
- Customer Retention Rate: This measures the percentage of customers that the company retains over a specified period. A high retention rate results in repeat purchases and increases brand loyalty.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): The NPS measures customer loyalty for the company. A high NPS indicates strong customer loyalty and the potential for organic growth through referrals and positive word of mouth.
- Churn Rate: This calculates the percentage of customers who stop doing business with your company over a certain period. High churn rates may indicate issues with product satisfaction or customer support, making it essential for businesses to address and reduce churn to maintain a healthy customer base.
- Upsell/Cross-Sell Rate: The upsell/cross-sell rate measures the percentage of existing customers who purchase additional products or services from your business. Monitoring this rate helps identify opportunities to offer complementary products or upgrades to existing customers, enhancing their overall experience and your bottom line.
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT): This is a metric to measure customer satisfaction. A CST score helps you identify areas for improvement in your products and customer service to further improve customer experience.
Final Word on Marketing Funnels
Make no mistake, creating a sales and marketing funnel using the process described above is no easy feat. This isn’t a project you’re going to complete in one afternoon — it’s a pursuit that you’ll want to actively address as long as your company is in business.
Creating a marketing funnel is not a simple undertaking, but it’s one of the few opportunities you have to drive significant improvements in your efficiency and effectiveness when closing deals.
Hopefully you learned how to build an effective marketing funnel, but if you just want an expert to do all the work for you, Single Grain can help!👇
Additional content contributed by Joydeep Bhattacharya
The post How to Build a Powerful Marketing Funnel (Step by Step) appeared first on Single Grain.